PATIENT ISOLATION
- PATIENT ISOLATION OVERVIEW
- AIR CHANGE CALCULATOR
- CASE STUDIES
- FACTS ABOUT TRUE HEPA FILTRATION
- FAQS
- LINKS & ARTICLES
- MEETING CDC AND AIA GUIDELINES
- MODES OF OPERATION
- NRTL SAFETY CERTIFICATION
- TECHNICAL ADVICE & PRODUCT QUESTIONS
- USING GERMICIDAL UV-C DISINFECTION
PATIENT ISOLATION
PURE AIR FOR HEALTHCARE®
Create CDC Compliant Surge Patient Isolation Capacity in Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities
Abatement Technologies® high-efficient HEPA-CARE® In-Room Air Purification Systems have set the gold standard for reliable and economical solutions that help hospitals and other healthcare facilities comply with CDC guidelines for airborne infection control. Learn how state-of-the-art patient isolation room equipment and products from Abatement Technologies can help create safer, cleaner environments for patients, staff and visitors.
Air Change Calculator for Abatement and Remediation
CASE STUDIES FOR PATIENT ISOLATION
ABATEMENT TECHNOLOGIES® HEPA-CARE® PORTABLE AND CEILING-MOUNTED AIR PURIFICATION SYSTEMS
DOUBLING ISOLATION ROOM CAPACITY AT NEW HAMPSHIRE HOSPITALS
A statewide survey by the New Hampshire Hospital Association revealed that hospitals had a low number of rooms available with both the capability of creating a negative pressure environment with 12 air changes per hour and the capability of cleansing the air through HEPA filters. CDC recommends that airborne infectious patients in a hospital should be isolated and cared for in rooms equipped with negative pressure and HEPA filtration. Negative pressure isolation rooms can also be used on a daily basis for various types of infectious diseases, including tuberculosis, Avian Influenza, and H1N1 swine flu, and for bioterrorism response.
Abatement Technologies® HEPA-CARE® Portable and Ceiling-Mounted Air Purification Systems were selected to create isolation rooms from standard patient rooms in all 26 acute care hospitals, New Hampshire Hospital and the VA Medical Center. The hospital selection committee, comprised of infection control and facilities professionals and emergency preparedness planners, chose Abatement Portable Air Purification models for the following reasons:
- Portability - Hospitals can easily choose which rooms in their facilities to convert to a negative pressure and HEPA filtered environment
- Effectiveness - Portable units can create an isolation room as effectively as a fixed unit in a fully renovated room
- Cost & Value - A portable unit is inexpensive compared to purchasing a fixed unit and renovating a single room
- Timing - The portable units were shipped to the hospitals and up and running within two weeks
Learn more background information on the Portable Isolation Units for New Hampshire’s Hospitals released by the NH Department of Health and Human Services and the New Hampshire Hospital Association. Read the press release announcing increased isolation room capacity in New Hampshire’s hospitals.
FACTS ABOUT TRUE HEPA FILTRATION
INFORMATION ON THE HEPA FILTERS EQUIPPED WITH ABATEMENT TECHNOLOGIES® HEPA-CARE® AIR PURIFICATION SYSTEMS
What does the term HEPA mean?
HEPA is an acronym for "High Efficiency Particulate Air" or "High Efficiency Particulate Arrestance." This acronym refers to a filter that is manufactured, tested, certified, and labeled in accordance with current HEPA filter standards. There are several sub-classes within the HEPA classification. The minimum HEPA category requires the filter to capture 99.97% of the 0.3-micron (0.000012-inch) particles in the air passing through the filter.
What is it that makes HEPA filters so efficient?
The ultra-fine, glass-fiber medium captures microscopic particles that can easily pass through other filters by a combination of diffusion, interception and inertial impaction. To meet the minimum requirements of a HEPA filter, the filter must be tested and certified to prove that it will remove at least 99.97% (9,997 out of 10,000) of particles 0.3-micron in diameter from the air passing through the filter. Particles that size are about 300 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair, and 25 to 50 times smaller than we can see. To a HEPA filter, catching a one-micron particle (1/1,000,000 of a meter) is the equivalent of stopping a cotton ball with a door screen.
Are all filters made with HEPA filter media HEPA filters?
No. Manufacturing a filter with HEPA filter media does not mean that the filter itself meets true HEPA efficiency requirements. Significant filter leakage can go undetected if filters are not individually tested and certified at the end of the manufacturing process. Even the tiniest pinhole leaks in the media or breach of the seal between the media pack and the filter frame can compromise the efficiency of the filter and cause it to fall below HEPA standards. Testing the completed filter in accordance with recognized industry standards is the only way to ensure the performance and integrity of that filter.
Are HEPA filters suitable for infectious patient isolation?
Yes. Current CDC Guidelines for Environmental Infection Control in Healthcare Facilities recommend HEPA filtration for the capture of pathogens, microbial spores and other contaminants in the air exhausted from patient isolation rooms.
Does HEPA filter efficiency decrease as the filter gets dirty?
No, quite the contrary. Unlike electrostatically-charged air filters and other technologies that experience substantial loss of efficiency as they become dirty, exactly the opposite typically happens with HEPA filters. The dirtier a HEPA filter gets, the more efficient it can become.
What are the pertinent testing & certification standards for HEPA filters?
Recommended practices for HEPA filter construction, performance, labeling and certification are maintained by the Institute of Environmental Sciences and Technology (IEST) and Underwriters Laboratories (UL). Primary requirements include:
- IEST-RP-CC021 “Testing HEPA and ULPA Media, which governs requirements for the filter media
- IEST-RP-CC001 “HEPA and ULPA Filters”, which governs overall filter construction and labeling requirements
- IEST-RP-CC034 “HEPA and ULPA Filter Leak Tests, which governs HEPA and ULPA filter penetration (leakage) tests
Testing and certification to meet UL900 flammability requirements is in-service efficiency testing also required or recommended?
Periodic testing (every 6 to 12 months) and testing whenever the HEPA filter is replaced are essential to ensuring that a HEPA filtration device continues to provide true HEPA efficiency. CDC Guidelines recommend such periodic testing and it is commonly required by facilities as well. It should also be noted that HEPA filters can begin to break down over time. Replacement every two years is highly recommended, even if the device is not used.
Why is HEPA testing done with a 0.3-micron particle size test aerosol?
Filter efficiency studies have shown that 0.3-microns is very close to what is known as the "Most Penetrating Particle Size (MPPS)" for HEPA filter media. Efficiency is typically greater than 99.97% against larger or smaller particle sizes. Particles larger than 0.3 microns are more easily trapped, or intercepted, by the media. Smaller particles often lack sufficient mass to penetrate the media. Most HEPA units have wood or particleboard frame HEPA filters.
Why are HEPA-CARE units equipped with metal frame HEPA filters?
CDC infection control guidelines recommend replacing wood frame filters in HVAC systems with metal frame filters due to the potential for microbial contamination that can potentially compromise air quality should the frame become and remain wet. We do not believe that HEPA filters with wood or fiberboard frames are suitable for critical infection-control applications either. They may be less costly initially, but in addition to microbial contamination wood frames are also far more susceptible to problems such as warping, cracking or distortion.
Do Abatement’s HEPA-CARE HEPA filters meet IEST & UL requirements?
Yes. In fact, our HEPA-CARE Air Purification Systems are actually equipped with high-efficiency HEPA filters that significantly exceed these requirements. These filters are tested and certified to 99.99% HEPA efficiency, which means that they remove at least 99.99% of particles as small 0.3 microns in size. In other words, permissible leakage (1 out of 10,000 particles) is 3 times lower than for a standard HEPA filter (3 out of 10,000 particles). The filters are constructed from microglass media in accordance with the IEST construction requirements and tested and labeled in accordance with IEST safety requirements and UL 900 flammability requirements.
Do HEPA-CARE pre-filters offer any added user benefits?
Yes. Cellulose-based filter media can become a fertile breeding ground for microbes. Our MERV 8 pre-filters are treated with an EPA registered, broad-spectrum anti-microbial designed to inhibit microbial growth and protect the integrity of the filter media.
How often do Abatement pre-filters and HEPA filters need to be changed?
The size and concentration of airborne contaminants, temperature, humidity conditions and duration of use determine how often filters need replacement. As all air filters become loaded with particulate matter, the static pressure differential across the filters will increase, and the airflow capacity of the air filtration device will decrease. To make operation simple, Abatement HEPA-CARE Air Purification Systems are equipped with separate, easy-to-read filter change indicator lamps for the pre-filter and the HEPA. Unlike gauges, these lamps do not require operator interpretation or calculations.
Abatement Technologies stocks a complete inventory of replacement filters, accessories and additional products for same or next day shipment. Contact Us or call us to receive filter pricing and availability information.
FAQS ABOUT EQUIPMENT FOR INFECTIOUS PATIENT ISOLATION
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT ABATEMENT TECHNOLOGIES® HEPA-CARE® AIR PURIFICATION SYSTEMS FOR MEETING CDC GUIDELINES FOR AIRBORNE INFECTION CONTROL AND HRSA SURGE CAPACITY PLANNING
How much experience does Abatement Technologies have in the healthcare market?
Abatement Technologies has sold critical air filtration equipment to hospitals, clinics and other health-related facilities since the mid-1980s. We developed our first HEPA-CARE systems for infectious patient isolation rooms in 1992. Since then we have worked with more than 5,000 facilities throughout the U.S., Canada and overseas to help them solve their infection control requirements in a timely and cost-effective manner.
How do we determine which HEPA-CARE Air Purification System is best for our facility?
Our experienced sales consultants can help you decide which model or models to select, and what other accessory products are required or recommended. Abatement HEPA-Care Portable units, which can be relocated from room-to-room as needed, provide maximum flexibility, and are therefore ideal for shorter term surge-capacity requirements. As a general rule of thumb, our HC800C Ceiling-Mounted Model is ideal for longer term applications because it is completely out of the way of staff, and takes up no floor space. It can also be used to meet CDC requirements for point-of-use HEPA filtration of supply air to positive pressure isolation rooms (PE). Both types of units are designed for point-of-use HEPA filtration of exhaust air from negative pressure AIIR rooms.
Why can’t we just buy commercial portable air cleaners to meet our requirements?
Unlike HEPA-CARE systems, general-purpose recirculating air cleaners are simply not designed to meet the critical infection control requirements in accordance with CDC, UL, CSA, OSHA and AIA. Features include true, metal-frame HEPA filters that are 100% tested to ensure that they provide minimum filtration efficiency of 99.99% @ 0.3 microns, “zero bypass” construction, and the ability to operate in negative pressure, positive pressure and recirculation modes. HEPA-CARE Air Purification Systems are Class II medical devices and are safety certified by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory.
Aren’t all HEPA filters pretty much the same?
Absolutely not. In many units, HEPA media filters are constructed with inexpensive particleboard frames that can warp, crack, off-gas and support microbial growth. In many instances, completed filters are not tested in accordance with Institute of Environmental Sciences and Technology IEST-RP-CC001.3 and MIL-STD 282. Damage to the media pack or leakage between the media pack and the filter frame that might compromise overall efficiency can therefore go undetected. The true Type C (99.99% efficiency @ 0.3 microns) gel seal HEPA-CARE filters are constructed with extruded anodized aluminum or galvanized steel frames, have a UL900 Class I flammability rating and meet IEST and MIL standards, including 100% testing. The unique silicone gel seal provides a more secure, bypass-free seal than other designs. Read the facts about true HEPA filtration.
How often should I change the HEPA-CARE filters?
This will vary depending on the size and concentration of contaminants, temperature and humidity conditions, and duration of use, but “change pre-filter” and “change HEPA” LEDs on the electronic control panel of our HEPA-CARE systems eliminates any guesswork. With continuous use, average primary filter life is one to two months. Timely filter changes are essential. When filters become loaded with particulate matter, the static pressure differential across the filters increases and the airflow output of the unit decreases. Regardless of the amount of use, the HEPA filter should be replaced every two years to ensure ongoing performance.
Are tools required for filter changes?
A ½” hex wrench is needed to access the filter compartment and prevent unauthorized access. Once this is done, filters are extremely easy to change and no tools are required.
Does changing filters in the Abatement HEPA-CARE ceiling mounted unit require removing ceiling tiles?
No. All HC800C filters are room-side accessible via a hinged, swing-down access door, so tiles do not need to be disturbed. The same holds true for the UV lamps in the UV400C-PT and UV400C UV modules.
How long should I run the HEPA-CARE unit between patients?
The CDC recommends 99.9% removal efficiency in the patient room. With 12 ACH, the waiting time should be approximately 30 to 40 minutes, but a one-hour minimum is a good policy adopted by numerous health care facilities.
How can Abatement Technologies products help us meet the most recent CDC Infection Control Guidelines?
Click to learn how Abatement Technologies solutions can help your facility meet CDC Guidelines for Environmental Infection Control in Health-Care Facilities.
Do the HEPA-CARE systems come fully equipped for negative pressure operation?
Complete, pre-packaged isolation room kits including the HEPA-CARE unit, a pressure monitor and other accessories are available.
Should we exhaust the filtered air from an isolation room outdoors?
Yes, if possible. It is always preferable to exhaust HEPA filtered air to the outdoors as an added safeguard, though indoor exhaust is permissible under CDC Guidelines for AIIR rooms, which state: “Direct exhaust air to the outside, away from air-intake and populated areas. If this is not practical, air from the room can be recirculated after passing through a HEPA filter.” However, it is also important to check your state regulations, because many states do not permit recirculation. As a result, very few infectious patient isolation installations recirculate, except in emergency circumstances.
What if we have an emergency requirement where we can’t exhaust outdoors?
Abatement Technologies offers several potential solutions. One is to place a portable HEPA-CARE model in the room and duct the HEPA-filtered air above the drop ceiling via one of our ceiling exhaust plates. We would recommend either using the HC800F with the HC600FUV model. Another is to duct the filtered exhaust air into a corridor. A third is to install an Abatement IQ200 Bed Isolation Tent around the patient bed, use an ISOQUAD® IQ200 module. The filtered air is simply exhausted back into the room. We recommend selecting one of these solutions in advance and purchasing the equipment so it is on site and ready to go in advance of such an emergency.
Our facility has combination negative/positive isolation rooms. Do they still meet CDC Guidelines?
Not any longer. The 2003 CDC Guidelines describe these rooms as “unreliable”, especially in the negative pressure mode, and specifically recommend against their use in new construction or renovations. The Guidelines also discourage the use of these rooms in existing facilities.
How many air changes per hour (ACH) do we need, and how do we determine how many HEPA-CARE units we need to provide the required ACH?
CDC requires at least 12 ACH in any renovated or new isolation rooms (PE or AIIR), a minimum of 6 ACH in existing isolation rooms and at least 15 ACH in operating rooms (including 3+cfm of fresh air). Most facilities target at least 12 ACH even in existing rooms. One or more HEPA-CARE systems may be needed, depending on the size of the room in cubic feet (length x width x height to the drop ceiling). As with any air filtration device (AFD), factors such as filter loading, attached collars or ducting and reduced voltage to the motors will decrease actual delivered airflow. Click for the Air Change Calculator to determine the number of HEPA-CARE units needed to produce ACH.
How can we factor in and compensate for these conditions?
Too much airflow is always better than not enough. Add as much safety margin as is practical within your budget, especially where long duct runs are required. A good rule of thumb is to design for 25% to 50% or more ACH than required to compensate for potential airflow losses–the more the better. In other words, if 12 air changes are the objective, design for at least 15 to 18 ACH. For information on the number of Abatement HEPA-CARE units required for various room sizes, please click for the Air Change Calculator.
How is the Abatement HEPA-CARE system disinfected after use?
We recommend that you wipe down the system with a water-based germicidal. Although changing the pre-filters between patients is not required, it is recommended for portable units that could be moved to another room. If filters are not changed in portable units, it is advisable to seal off the openings around the inlet door before the unit is moved. Many facilities replace the pre-filters between patients in all units, including ceiling mounted models.
How often do we need to have the HEPA-CARE units tested?
The 1994 CDC TB Guidelines recommend quantitative leakage and filter performance testing after installation and every six months thereafter, or whenever the HEPA is replaced. This is a good guideline. Most facilities use the same company that tests and certifies biological safety cabinets.
Where should the system be located in the patient's room?
Abatement Portable In-Room Systems should be positioned at a maximum distance from the door to the corridor so as to create a directional airflow away from the corridor and the healthcare worker. Abatement Ceiling-Mounted Systems are generally installed over the patient's bed and should be located as far as possible away from the room supply air diffuser to minimize "short-circuiting" of air.
What is "short-circuiting"?
Short-circuiting occurs when the air supplied to the room by the facility HVAC system passes directly into the HEPA Filtration System without first being circulated through the room. This can reduce the effectiveness of the system for reducing airborne concentrations of TB droplet nuclei within the room.
Is pressure monitoring required?
Yes. CDC requires daily room differential-pressure monitoring, but this may be insufficient to catch pressurization problems on a timely basis. Our state-of-the-art continuous electronic monitors eliminate the need for daily, time-consuming smoke tube testing, provide continuous real-time monitoring, and a 24/7 record of these conditions. Learn more about Abatement Technologies HEPA-CARE Room Air Pressure Monitors for Negative or Positive Pressure Patient Isolation Rooms.
Are anterooms required?
In general, the CDC Guidelines include design parameters for isolation rooms with and without anterooms. Anterooms are recommended for certain special situations, such as isolating a TB patient after surgery, or isolating smallpox or viral hemorrhagic fever (VHF) patients. The 2003 CDC Guidelines illustrate two options for these situations, one with a neutral anteroom and one with an anteroom under negative pressure related to both the patient room and the corridor. If a room with an anteroom is not available, CDC recommends using portable HEPA units in the room to provide additional ACH equivalents. Learn more about Portable Anteroom Modules from Abatement Technologies.
Does my isolation room need to be tightly sealed?
No. Isolation rooms depend on air that infiltrates into the room (for negative pressure) or out of the room (positive pressure) through the gap under the door and through other small openings. It is not necessary to replace drop ceilings with solid ceilings to maintain sufficient differential pressure and ACH.
What is the estimated shipping time of your HEPA-CARE systems?
We do our best to keep enough inventory on-hand for shipment within 24 hours. Very large orders that must ship complete may require additional time. Approximate transit time within the continental United States is two to seven days. You will be notified if there are any anticipated delays at the time of order placement.
What is the warranty of Abatement HEPA-CARE Air Purification Systems?
Abatement stands behind its products. All systems are covered by a comprehensive limited warranty to the original user against defects in materials and workmanship for a period of two years after date of purchase. Over the past 20+ years HEPA-CARE systems have proven to be extremely reliable, and both warranty and non-warranty repair requirements have been very minimal.
Do the CDC SARS Guidelines differ significantly from the CDC TB recommendations?
No. Similar precautions are recommended, including isolating suspected or known infected patients in negative pressure AIIR rooms. The same principles hold true for avian influenza, swine flu or any other infectious organism with the potential for airborne transmission.
Is the effectiveness of HVAC-mounted germicidal UV lamps against airborne bacteria and viruses been recognized by health professionals?
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Infection Control Guidelines recognize the effectiveness of ultraviolet germicidal irradiation (UVGI) lamps for providing supplemental protection and effective ACH when mounted in upper room air or connected into the facility HVAC system. Abatement Technologies offers four UVGI options, including: the UV800F, which mounts onto our HC600FUV HEPA-CARE model; and, our ceiling-mounted UV400C-PT and UV400C UVGI modules.
How do the requirements for patient isolation during bioterrorism response differ from H1N1 or SARS?
In most instances they are virtually identical: identify infectious or potentially infectious patients, and isolate them in negative pressure infectious patient isolation rooms. The same principles apply. That’s what makes HEPA-CARE systems so versatile.
What do you mean by “aircraft type construction”?
Fasteners such as sheet metal screws and hollow pop rivets are cheaper and easier to use, but they provide potential leakage points for sub-micron particles and bio-pollutants. HEPA-CARE devices are constructed using aircraft grade aluminum cabinets, solid leak-proof aircraft type aluminum rivets and sealed critical seams. In addition, in most air filtration devices, the section of the cabinet downstream from the HEPA filter remains under negative pressure (a vacuum). This means that “dirty” room air can be pulled into the cabinet and exhausted without ever passing through the HEPA. HEPA-CARE units maintain positive pressure downstream from the HEPA to ensure that dirty room air can’t leak into that section of the cabinet.
FAQS ABOUT KILLING MICROORGANISMS ON A HEPA FILTER WITH UV-C LAMPS
How is UV-C exposure quantified?
UV dosage, which is typically expressed in microwatts per square centimeter, is based on four factors:
- Direct exposure to the UV-C irradiation source
- The intensity of the UV-C source
- The distance away from that source
- The duration of exposure
Because organisms in rapidly moving airstreams are exposed to the UV-C source for only fractions of a second, effective disinfection requires very high-intensity UV-C output and very close proximity to the lamps. This is especially true for more complex organisms such as fungi, which typically require five to 20 times more UV-C energy to destroy than bacteria.
Why is proximity to the lamp so important?
Studies have shown that UV-C dosage decreases by approximately the square of the distance from the lamp. In other words, compared to dosage one inch away from the lamp, dosage is four times lower at 2 inches away, sixty-four times lower at 8 inches away and 144 times lower at 12 inches away. In some air filtration systems, organisms that pass the lamps or are trapped on the media can be as far as 12 to 48 inches away from the lamp.
Can UV lamps shining on the inlet face of a HEPA filter kill all of the organisms trapped on the media?
This would be highly doubtful because the lamp can't kill what it can't "see". HEPA filters are designed with very closely spaced pleats, with typical pack depths of anywhere from three to four inches up to 12 inches. It's highly unlikely that a lamp or lamps shining on the inlet face of a HEPA filter would expose microorganisms trapped on the inlet surfaces of the pleated media pack much beyond the first half-inch to one inch of depth, especially for pleats that are farthest away from the lamp(s). As a result, effectiveness would likely be limited to only a small percentage of the media area.
Why should contaminated air be filtered before it reaches the lamp(s)?
Filtration systems that do not pre-filter air before it gets to the lamp(s) and the HEPA filter can expose the lamp(s) to larger dust and dirt particles. This can result in the formation of a dirt film deposit on the quartz glass and significantly reduced UV-C intensity. In addition, agglomerated dirt particles that form on the HEPA filter media can reduce airflow and filter capacity, shorten filter life and further block UV-C exposure to organisms that may be trapped beneath them. With the design of an Abatement HEPA-CARE Air Purification System, air is pre-filtered and HEPA-filtered before it is exhausted into the UV-C module, thus maximizing UV intensity to kill microorganisms.
Couldn’t a pre-filter be used to reduce lamp-contamination problems for the internal lamp systems?
Yes, but then the pre-filter media must be protected from exposure to the lamp(s). High-intensity UV-C radiation can rapidly break down and pulverize most pre-filter media, especially synthetics, cotton and blends. Exposed components such as electrical wiring and rubber gaskets can also be degraded if not protected properly. HEPA media is much more UV-resistant, but lamps must be still kept far enough away from the media to ensure that the UV-C energy won’t destroy filter integrity by breaking down filter binders and adhesives, and won’t cause VOC off-gassing.
How are patients and workers properly protected from accidental UV exposure?
Because direct UV-C lamp exposure can seriously damage the eyes or the skin, extra precautions are needed to ensure that patients, healthcare workers or maintenance personnel are not exposed to the UV-C lamps during normal use or when replacing filters. This is a much more difficult task when the lamps are located on the inlet side of the HEPA filter. With our design, the separate UV-C modules keep the lamps isolated from the filter compartment and are accessed only about once a year for lamp replacement. Built-in safeguards, such as electrical interlock switches, instantly deactivate the lamps when the access door is opened. It is also very important to ensure that the overall unit has been safety tested and certified by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) such as UL, ETL or CSA. Abatement's germicidal UV-C modules meet this requirement.
FAQS ABOUT PRODUCT SAFETY CERTIFICATION
You really emphasize the fact that Abatement products are tested and certified by ETL, a Nationally recognized testing Laboratory (NRTL). What are the requirements?
In the USA, OSHA safety standards for general industry and construction and the National Electrical Code require testing and listing (certification) of electrical products to applicable standards. It is important to note that this testing must be performed on an electrical device even if the individual electrical components used in that device are all listed or approved. Testing must be done by an OSHA-recognized NRTL, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories), ETL (Environmental Testing Laboratories) or CSA (Canadian Standards Association). In Canada, The Standards Council of Canada has adopted standards for the Canadian Electrical Code developed on its behalf by the Canadian Standards Association (CSA). Third party testing from a laboratory or other organization, not NRTL-certified is not acceptable, even if such testing is done to applicable standards.
Why is NRTL certification so important?
Unless a unit is properly tested, users have no way of knowing whether it is properly and safely designed to meet the requirements of the applicable electrical codes. It is wise to require written vendor verification that the products you purchase are NRTL certified. Learn more about NRTL safety certification in healthcare facilities.
Aren't all air filtration products properly certified?
No. Unfortunately, many of the air filtration systems sold to and used by contractors, healthcare facilities and others are not certified, especially negative air machines.
LINKS AND ARTICLES ON INFECTIOUS PATIENT ISOLATION
BIOTERRORISM PLANNING AND RESPONSE (AHRQ)
Biological and Chemical Terrorism Information for Healthcare Professionals
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory – “Advice for Safeguarding Buildings Against Chemical or Biological Attacks”
INFECTION CONTROL ISOLATION GUIDELINES
INFECTION CONTROL DURING RENOVATION & CONSTRUCTION
Infection Control Today - “Control the Chaos and the Spread of Infection During Construction”
Health Facilities Management, July 2002 - "Clean Construction: Advice on Controlling Infection Risks During Building Projects"
U.S. EPA Indoor Air Quality-Mold Site ”
APIC State-of-the-Art Report: The Role of Infection Control During Construction in Health Care Facilities - APIC SOAR Construction 2000”
INFECTIOUS DISEASES
US Government Avian Flu and Pandemic Flu Information
National Strategy for Pandemic Influenza
Carl C. Schultz, P.E. - "TB, SARS, and the Surgical Suite; Engineered Systems"
CDC Division of Tuberculosis Elimination (DTBE) - News & Updates
ISOLATION ROOMS
Francis Curry: Isolation Rooms Design, Assessment and Upgrade
Using Germicidal UV Disinfection - Alternative Methods for Using Germicidal UV Disinfection Lamps to Supplement HEPA Filtration
Isolation Room Monitor Checklist
PROFESSIONAL ORGANIZATIONS AND ASSOCIATIONS
American Society for Healthcare Engineering - www.ashe.org/
Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology - www.apic.org
American Institute of Architects - www.aia.org
U.S. GOVERNMENT AGENCIES
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention - www.cdc.gov
Department of Homeland Security - www.dhs.gov
Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Emergency (PHE) - www.phe.gov
National Disaster Medical System (NDMS) - www.phe.gov/ndms
FOR CANADA
Government of Canada - Pandemic Influenza
Public Health Agency of Canada - Avian Flu
Construction-Related Nosocomial Infections in Patients in Health Care Facilities - Canada Construction Related Guidelines
MEETING CDC AND AIA GUIDELINES FOR HEALTHCARE INFECTION CONTROL
CREATE SAFER PATIENT ENVIRONMENTS
Abatement Technologies® HEPA-CARE® Air Purification Systems and related products are designed to help healthcare facilities create safer patient environments and meet stringent CDC, AIA and Canadian CSA/CCDR Guidelines for healthcare infection control in venues where healthcare is provided such as:
- Acute Care Facilities
- Outpatient Surgical Centers
- Urgent Care Centers
- Clinics
- Outpatient Dialysis Centers
- Physician's Offices
- Skilled Nursing Facilities
DETERMINING PROTECTIVE MEASURES REQUIRED BY AN ICRA
In 2003 the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and HICPAC (Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee) published updated Guidelines for Infection Control in Health-Care Facilities. HICPAC is a 12-member group that advises CDC on ways to help prevent opportunistic, environmentally related infections in immunocompromised patients.
The guidelines incorporate standards from other organizations, including the American Institute of Architects (AIA) and American Society of Heating, Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE), as well as relevant regulations from federal agencies such as FDA, OSHA and EPA.
The tables in the link below illustrate some of the ways that healthcare facilities utilize Abatement Technologies products to meet certain engineering provisions for various infection control applications including:
- Airborne Infectious Isolation (AIIR) Rooms
- Protective Environments (PE)
- Operating Rooms & Laser Surgery
- Air Handling Systems
ABATEMENT TECHNOLOGIES SOLUTIONS FOR AIRBORNE INFECTIOUS ISOLATION ROOMS
Negative Pressure Patient Isolation - Download our Guide to Meeting CDC and AIA Guidelines for Healthcare Infection Control
CANADIAN STANDARDS FOR HEALTH CARE CONSTRUCTION ( CANADA HEALTHCARE FACILITIES)
The Canadian Standards Association (CSA) has also developed and implemented similar standards for Canadian health care facilities. The Canadian Standards association (CSA) has issued CSA Z317.13-03 Infection Control During Construction or Renovation of Health Care Facilities, which outlines similar requirements for Canadian healthcare settings.
They also led to the 2007 development and implementation of CSA (Canadian Standards Association) standard CAN/CSA-Z317.13-07 for Canadian facilities.
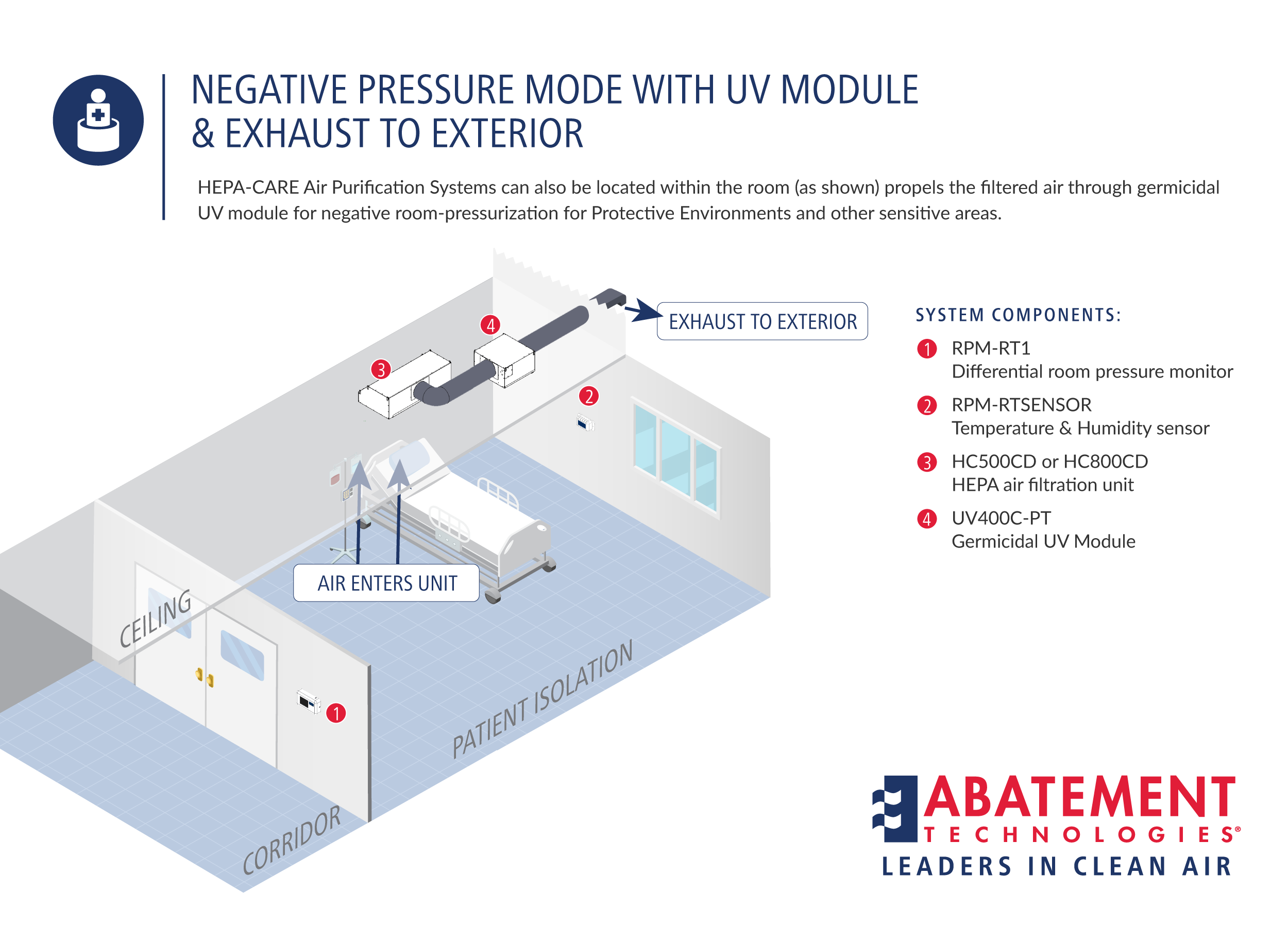
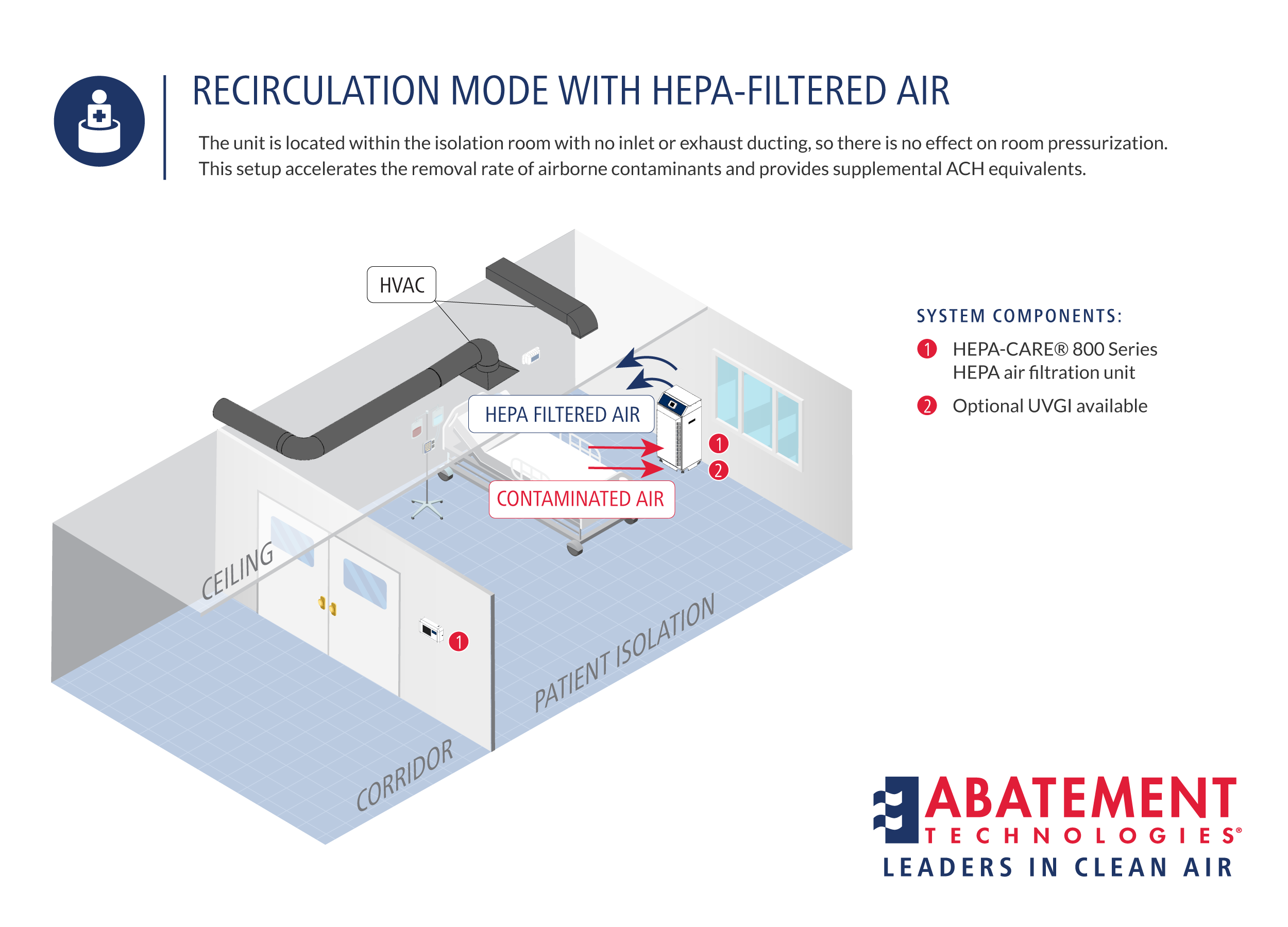
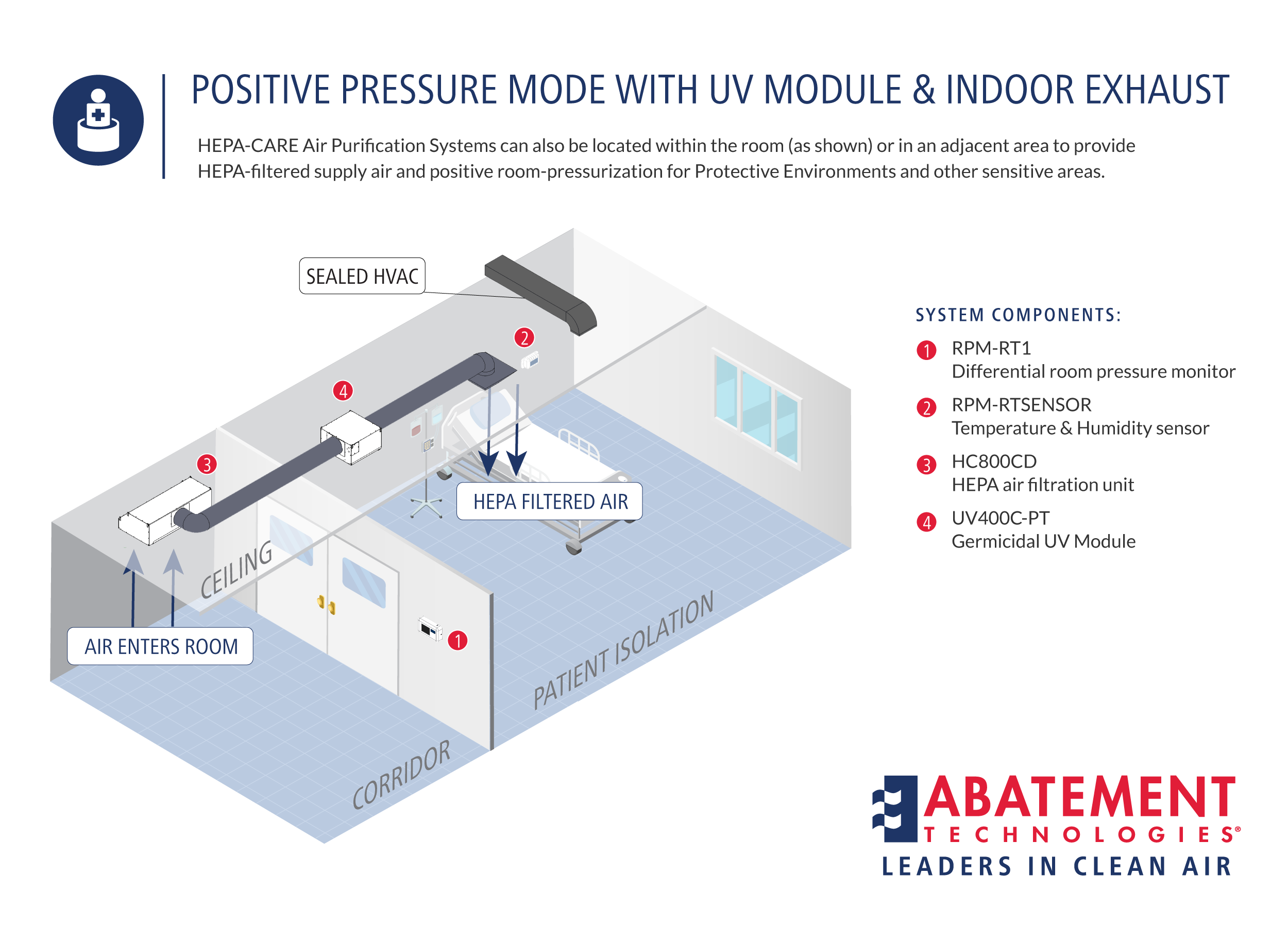
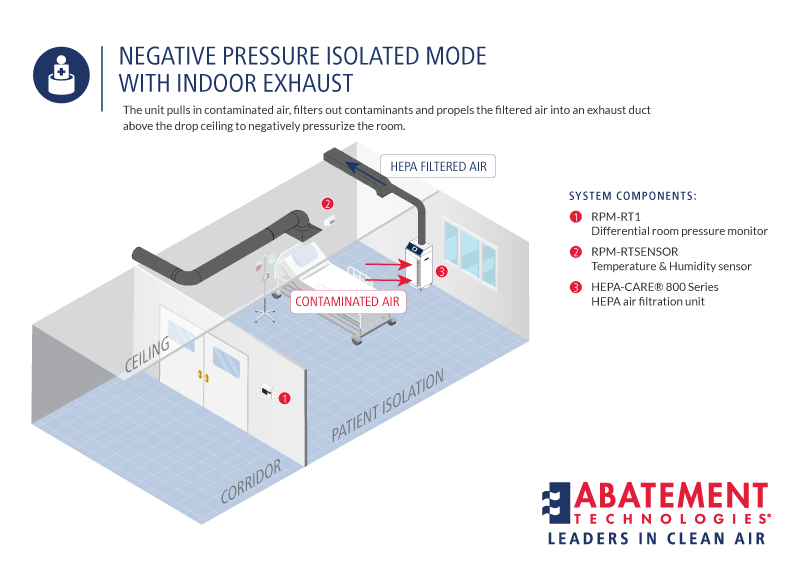
MODES OF OPERATION
State-of-the-art Portable Air Scrubbers from Abatement Technologies can be used in any of these modes of operation, depending on the air cleansing objectives and space limitations:
1.
|
|
2.
|
|
3.
|
|
4.
|
NRTL PRODUCT SAFETY CERTIFICATION IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES
Abatement Technologies® HEPA-CARE® Air Purification Systems have been tested by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL), and carry the appropriate marks certifying that they comply with applicable OSHA and CSA electrical safety standards.
Required Testing and Certification of Electrical Products
In the USA, OSHA safety standards for general industry and construction and the National Electrical Code require testing and listing (certification) of electrical products to applicable standards. It is important to note that this testing must be performed on an electrical device even if the individual electrical components used in that device are all listed or approved. Testing must be done by an OSHA-recognized NRTL, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories), ETL (Environmental Testing Laboratories), TÜV SÜD, or CSA (Canadian Standards Association). In Canada, The Standards Council of Canada has adopted standards for the Canadian Electrical Code developed on its behalf by the Canadian Standards Association
Why is NRTL Certification Important?
Unless a unit is properly tested, users have no way of knowing whether it is properly and safely designed to meet the requirements of the applicable electrical codes. It is wise to require written vendor verification that the products you purchase are NRTL certified.
Aren't All Air Filtration Products Properly Certified?
No. Unfortunately, many of the portable air scrubbers and air filtration systems sold to and used by contractors, healthcare facilities, and others are not certified. It is, therefore, impossible to know whether such products are safe or perhaps placing workers at risk.
TECHNICAL ADVICE & PRODUCT SALES QUESTIONS
CONTACT YOUR PRODUCT SPECIALIST FROM ABATEMENT TECHNOLOGIES®
Abatement Technologies’ product specialists are here to answer technical questions and help you make the right product choices. Product specialists are available Monday-Friday, 8:00 a.m. - 5:30 p.m. Eastern time.
UNITED STATES CUSTOMERS
Customers in the U.S. can call toll-free at 800-634-9091 and ask to speak with a product specialist, or e-mail: iaqinfo@abatement.com
CANADIAN CUSTOMERS
Customers in Canada can call toll-free at 800-827-6443 and ask to speak with a product specialist, or e-mail: iaqinfo@abatement.ca
INTERNATIONAL CUSTOMERS
International customers can call 678-889-4200 and ask to speak with a product specialist, or e-mail: iaqinfo@abatement.com
USING GERMICIDAL UV-C DISINFECTION
ALTERNATE METHODS FOR USING GERMICIAL UV-C DISINFECTION LAMPS TO SUPPLEMENT HEPA FILTRATION
Today, healthcare facilities must be prepared to face potential large-scale threats from chemical, biological, and nuclear contaminants that were almost unthinkable in the past.
HRSA Critical Benchmark #2-2 has significantly increased the surge isolation room capacity requirements for hospitals and clinics in an effort to handle a potential influx of potentially infectious patients. Existing capacities have been further strained by the recommendations in the 2003 CDC Guidelines.
Existing capacities have been further strained by the recommendations in the 2003 CDC Guidelines against the use of dual-purpose (positive/negative) isolation rooms in either new or existing facilities, because these rooms can be “unreliable.”
SHOULD YOUR FACILITY CONSIDER UVGI?
HEPA filtration, air changes, containment, and negative room-pressurization are the time-proven engineering measures for successful patient isolation and infection control. They remain the primary recommended controls under current and proposed standards for Airborne Infectious Isolation (AII) rooms and Protective Environments (PE).
Because of the unknown nature and toxicity of the pathogens that may be involved, an increasing number of facilities are also considering the use of UVGI (Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation) lamps, also called UV-C lamps, as an additional measure. Others remain wary because of safety and efficacy concerns.
Common questions from infection control and facility engineering professionals regarding this technology include the following:
- Do UVGI lamps really increase the level of protection?
- How much UVGI output is needed?
- Where should the lamps be located for maximum effectiveness?
- Can UVGI be used safely?
The purpose of this article is to help provide some of the answers.
The short answer is that UVGI disinfection can complement these other infection control measures. Leading hospital applications include:
- Providing an additional level of protection for patient isolation rooms.
- Continuous air disinfection in areas where the infectious status of patients may be unknown, such as ER, outpatient clinics, or waiting areas.
- Controlling airbone pathogens and odors to improve worker safety and comfort in areas such as laboratories, autopsy or morgue